
A Global as well as Local Flexibility Marketplace to Demonstrate Grid Balancing Mechanisms through Cross-sectoral Interconnected and Integrated Energy Ecosystems enabling Automatic Flexibility Trading
Local energy, global impact.


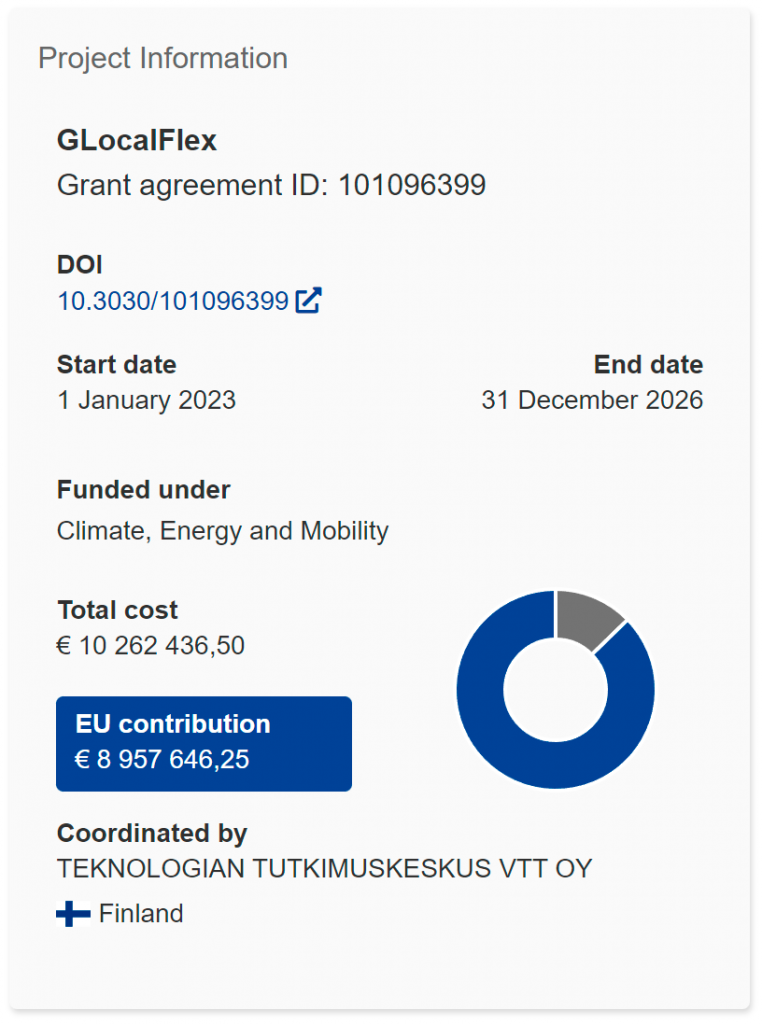
GENERAL FACTS ABOUT GLOCALFLEX
NAME
GLocalFlex
TYPE OF PROJECT
Horizon Europe Project
PROJECT DURATION
48 months
23 PARTICIPANTS
17 partners and 6 associated partners
8 COUNTRIES
Spain, France, Finland, Germany, Serbia, Czechia, Switzerland and Sweden
COORDINATOR
Teknologian Tutkimuskeskus VTT Oy

THE FUTURE OF ENERGY: SMART GRIDS, RENEWABLE SOURCES, AND ENERGY TRADING
Smart grid technology is transforming the way we generate, distribute, and consume energy. A smart grid is a modern electricity network that utilizes advanced sensors, communication systems, and automation to optimize the management of the grid. Smart grids can integrate renewable energy sources such as solar panels and wind turbines into the system and enable distributed generation, where electricity is generated at the point of consumption, reducing the need for large centralized power plants.
Hydrogen is another promising energy source that can be used in smart grids. It can be produced from renewable energy sources such as solar or wind power and used to power fuel cells for transportation or electricity generation.
Smart cities are urban areas that utilize smart grid technology and other innovative solutions to manage resources more efficiently and sustainably. They integrate energy, transportation, and communication systems to create a seamless, interconnected network. This can lead to reduced energy consumption, lower carbon emissions, and improved quality of life for residents.
The implementation of smart grids, distributed generation, and renewable energy sources is driving innovation in the energy sector. This has led to the development of new energy trading platforms that enable consumers to sell excess energy generated from their solar panels back to the grid. These platforms create new revenue streams for consumers and promote the adoption of green energy.
Projects such as GLocalFlex are exploring the potential of energy trading in smart grids to promote the scaling of flexible local energy systems (LES) and increase consumer participation in energy markets. Such projects are essential in creating a more sustainable energy future and promoting the adoption of innovative solutions in the energy sector.
In conclusion, the development of smart grids, distributed generation, renewable energy, and energy trading is driving innovation and creating a more sustainable future. Smart cities are leading the way in the implementation of these solutions, with many projects and clusters focusing on creating a more interconnected and efficient energy system for the future.
GLOCALFLEX PROJECT
GLocalFlex project aims to develop an energy flexibility marketplace integrated with several local energy systems, positive energy districts, cross-sectoral energy management systems, microgrids, electric transport, industries, individual consumers, and appliances.
The project aims to build on and upgrade existing energy systems to expose their flexibility potential to flexibility/demand response (DR) marketplace.
GLocalFlex consists of six heterogenous pilot sites demonstrating flexibility potential, solutions, and services ranging from consumers to industries, which interact with automated marketplaces to increase the participation of consumers at all grid levels.
The project demonstrates how cost-efficient flexibility markets can also operate without aggregators and how GLocalFlex solution has its place in supplementing co-existing flexibility solutions.
The proposed GLocalFlex flexibility marketplace has a neutral and well-defined rule base applicable to all energy stakeholders, and the GLocalFlex concept is driven by spot pricing, scalable, regulated, and diverse in terms of used technologies, participating entities, and business models.
The project also aims to replicate services in different business models and provides valuable information on business models needed for replication and the performance of replicated services.